Introduction Flint Population , MI Has Lost Over Half Its Since 1950:
Flint population , Michigan, once a thriving industrial hub, has experienced a dramatic decline in its population over the past seven decades. From its peak in the mid-20th century to the present day, Flint population has lost over half of its residents, leaving behind a city grappling with economic challenges, social disparities, and infrastructure decay. In this article, we’ll explore the factors contributing to Flint population decline, examine the implications for residents and the community, and discuss efforts to revitalize the city in the face of adversity.
The Rise and Fall of Flint Population:
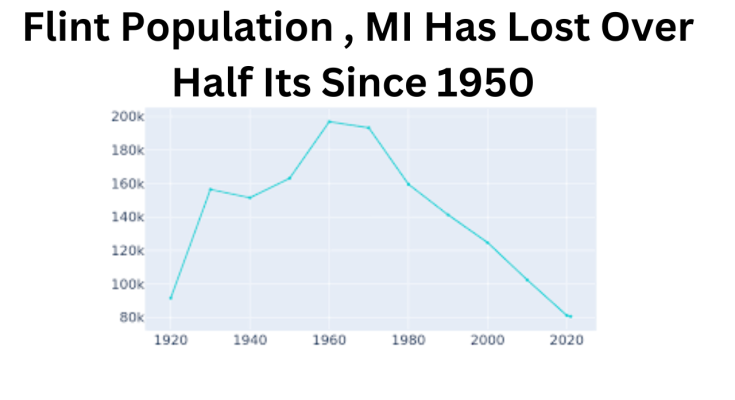
In the post-World War II era, Flint population experienced unprecedented growth and prosperity, fueled by the booming automotive industry and the presence of manufacturing giants like General Motors. During its peak in the 1950s, Flint was home to over 200,000 residents, drawn to the promise of stable jobs, affordable housing, and a vibrant community.
However, the fortunes of Flint population began to decline in the latter half of the 20th century, as economic shifts, industrial restructuring, and demographic changes took their toll on the city. The decline of the automotive industry, coupled with factors such as suburbanization, deindustrialization, and racial tensions, led to a steady exodus of residents from Flint.
By the turn of the 21st century, Flint population had plummeted to less than half of its peak, with many residents fleeing to suburban areas in search of better opportunities and improved quality of life. Today, Flint population continues to grapple with the legacy of its population decline, facing challenges ranging from blighted neighborhoods to strained public services and declining property values.
Read More Article : Quarantine Rules: Understanding rule 2.13 in new york
Factors Contributing to Flint Population Decline:
Several factors have contributed to Flint population decline over the past several decades:
- Economic Disinvestment: The decline of the automotive industry and the departure of manufacturing plants from Flint left many residents without stable employment opportunities, leading to job losses, wage stagnation, and economic disinvestment in the city.
- Urban Decay and Blight: The exodus of residents from Flint population has left behind vacant and abandoned properties, contributing to urban decay, blight, and disinvestment in neighborhoods. Vacant lots and derelict buildings dot the landscape, undermining community cohesion and exacerbating social challenges.
- Racial Segregation and Disparities: Flint population decline has been marked by racial segregation and disparities, with African American residents disproportionately affected by economic hardship, unemployment, and poverty. Persistent racial inequalities have hindered efforts to address systemic issues and promote equitable development in the city.
Implications for Residents and the Community:
The population decline in Flint has had far-reaching implications for residents and the community as a whole:
- Economic Challenges: Flint’s shrinking population has strained the city’s tax base, limiting resources for essential services such as education, healthcare, and public safety. Declining property values and dwindling business opportunities further compound economic challenges for residents and local businesses.
- Social Dislocation: The exodus of residents from Flint has led to social dislocation and community fragmentation, as families are uprooted from their neighborhoods and support networks. Social cohesion and collective resilience are weakened, making it difficult to address shared challenges and foster community empowerment.
- Infrastructure Decay: As Flint’s population has declined, the city’s infrastructure has suffered from neglect and disinvestment. Aging water systems, deteriorating roads and bridges, and inadequate public transportation infrastructure pose significant challenges to residents’ quality of life and safety.
Efforts to Revitalize Flint:
Despite its challenges, Flint has seen renewed efforts to revitalize the city and address the root causes of its population decline:
- Economic Diversification: Efforts to diversify Flint’s economy beyond manufacturing have focused on attracting new industries, supporting small businesses, and fostering entrepreneurship. Initiatives such as business incubators, workforce development programs, and investment in innovation hubs aim to create new economic opportunities for residents.
- Neighborhood Revitalization: Community-led efforts to revitalize neighborhoods and combat blight have gained momentum in Flint. Programs focused on rehabilitating vacant properties, beautifying public spaces, and fostering community engagement aim to strengthen neighborhoods and rebuild social capital.
- Addressing Public Health Challenges: The Flint water crisis, which exposed residents to lead-contaminated water, highlighted the urgent need to address public health challenges in the city. Investments in clean water infrastructure, healthcare access, and environmental remediation are essential for safeguarding residents’ health and well-being.
Conclusion Flint Population , MI Has Lost Over Half Its Since 1950:
The population decline in Flint, Michigan, is a poignant reminder of the complex challenges facing post-industrial cities in the United States. From economic disinvestment to social disparities and infrastructure decay, Flint has grappled with the consequences of its shrinking population for decades. However, amidst the challenges, there are signs of hope and resilience as residents, community organizations, and policymakers work together to revitalize the city and build a brighter future for all.
Read More Interesting Article : Flint, MI Has Lost Over Half Its Population Since 1950